Plants and Light – Units and Factors
For plants to live they need water, some nutrients and above all light. The light is essential for the survival, growth and yield of a plant and should therefore not be underestimated. What exactly is light, what is photometry and how do I find the right one?
With photometryor photometry(altgr. •phos‹light‹ and ‹meterin‹measure‹ are called measurementmethods in the wavelength range of the visible lightby means of a photometer[Wikipedia].
In this article I will give a small overview of the different properties of light and show which values and units are important for the plants.
photometry
Light can be measured naturally. Just like weight. length or heat. Unfortunately, in the case of light, not only one unit is enough to describe it. There are a few factors to consider:
- Brightness
- Light
- Spectrum (light waves)
- Color
- our feelings
Our perception is very important, because it is a difference how bright, warm or brilliant a light is and how it is perceived individually at the end. This is why, for example, the brightness and brightness of a lamp are distinguished.
The light rays, or rather, the brightness of a light source is measured in 3 ranges. Since light always travels a path, its origin, its path and its goal must be measured. The origin is measured inluminous flux (lumens). The path the light travels is defined as the luminous intensity (candela) and its targetilluminance (lux).
In order to illuminate a plant wall, the illuminance (LUX) is of particular interest. However, since you can only measure them with a luxmeter on site, it is also important to know what the other values say, because these are the ones that are often found on the packaging of lamps.
Luminous flux
The luminous flux of a lamp describes the sum of all light rays emitted by a lamp and is described in lumens. Lumens are always measured directly at the light source. The lumens are measured in the light laboratory and the value is indicated on the packaging. Lumen (Latin for light, luminaire) gives information about the brightness of a light source as a whole but not about the intensity of the light. Lumens can say how bright it becomes in the whole room, but not how bright it is in certain areas/places in the home.
Lumen is particularly interesting when it comes to the efficiency of a light source. The more lumens emitted per watt, the greater the energy efficiency of the lamp.
luminous intensity
Luminous intensity is the path of light. Not only the brightness (lumen) is measured, but also the radiation angle. Thus the luminous intensity indicates not only how much light the lamp emits, but also where it goes. In addition, the intensity with which the light radiates can be seen. The more the light can radiate around a light source, the smaller the candela. If the light is bundled and can only radiate in a given direction, the candela increases.
The luminous intensity is measured in candela (cd) and corresponds to the light that radiates in a certain area (steradian¹). 1 Candela corresponds to the luminous intensity of a candle. A headlight can have up to 70’000 Candela.
illumination
So far we know how much light a light source emits. But how much of it really arrives at the plant wall?
Illuminancerefers to the amount of light that hits the illuminated surface at the end. This amount of light is indicated in lux. This illuminance can be measured directly on the surface with a lux meter. In addition, many lamp manufacturers provide a luminous efficacy graph that shows how much lux arrives at a certain point.
It is also possible to calculate the illuminance. We have provided a calculator for this on our Vivit homepage:https://vivit.green/vertikalbegruenung-pflanzenlicht-planung-berechnung-online-kalkulator/
Lux
The amount of light incident on the illuminated surface is measured in lux. Actually only Lux is interested in the brightness. Since the lux value depends strongly on the distance to the light source, there is not simply a lux value for a lamp. It must always be determined for the respective lighting situation.
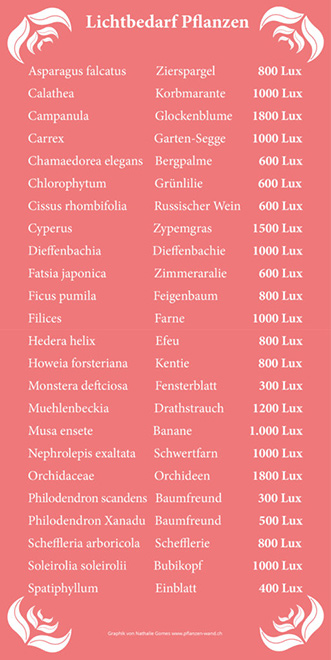
Roughly speaking, lux values can be divided into the following plant categories:
- Bright – 2000-3000 Lux
- Half-shaded – 1000-2000 Lux
- Shaded – 500-1000 Lux
Since it is very difficult for an untrained eye to estimate how much lux really radiates on a surface, it is recommended to measure the lux. There are luxmetersand now even apps (although some of them require a light measurement accessory).
My tip
A vertical indoor garden needs at least 1000 lux on the vegetation surface.
Hell (2000-3000 Lux)
Begonias, bananas, strelitzias, euphorbias, birch fig (Ficus benjamina), hydrangeas, Christmas stars, carnivorous plants, cacti and succulents, alpine veils, azaleas.
Half-shaded (1000-2000 Lux)
Orchids, Alokasia, Calathea, Window Leaf, Lucky Chestnut, Ornamental Pepper, Ufo Plant, Tree Friend (Philodendron), Radiant Aralie (Schefflera), Most Palms
Shaded (500-1000 Lux)
Diefenbachie, Zamie, Bow Hemp, Dragon Trees, Piston Thread, Single Leaf

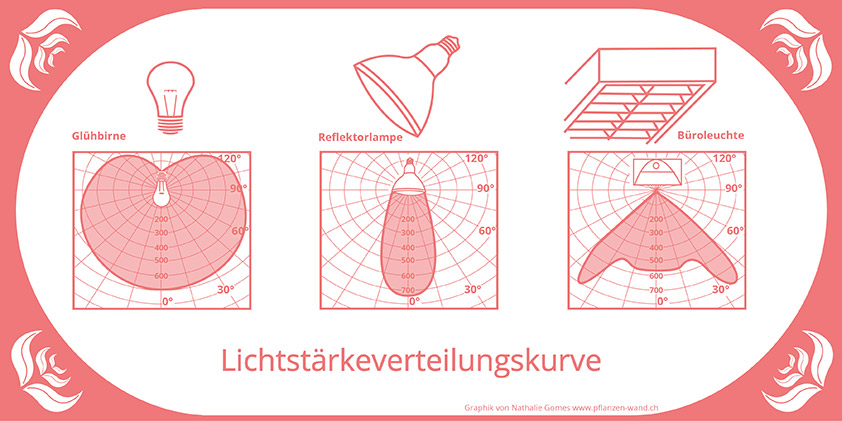
Light distribution curve
Many lamp manufacturers offer a luminous intensity version curve (LSVK) for the respective lamp. This allows the lux value to be read without measuring. Unfortunately, these curves are rarely printed on the packaging and need to be requested. These light distribution curves are a visual representation of the light distribution of a lamp. They indicate how much light is present at which location (distance and angle to the lamp). This luminous intensity is represented in lumens and is listed with the angles (degrees) in the schema. Radiating from the light source, the room angles and radial are around the light source.
In the upper picture I have 3 examples that show how different the different LSVK’s look of the different lamps.
But what do the lumen values determined say?
They provide information about the amount of light at a specific location in an ideal space. This means that they do not include light-swallowing and reflective elements such as furniture or wallpaper, nor nichesor walls that protrude into the room as a result.
When buying a lamp, this curve can help to…
- … to estimate whether the plant wall can be illuminated evenly
- … the ideal distance and position of the lamp to the plant wall
- … compare the height of the luminous intensity with other lamps, taking into account your own lighting situation.
Example. I only have the possibility to mount a lamp 1.2m away from the plant wall on the ceiling.
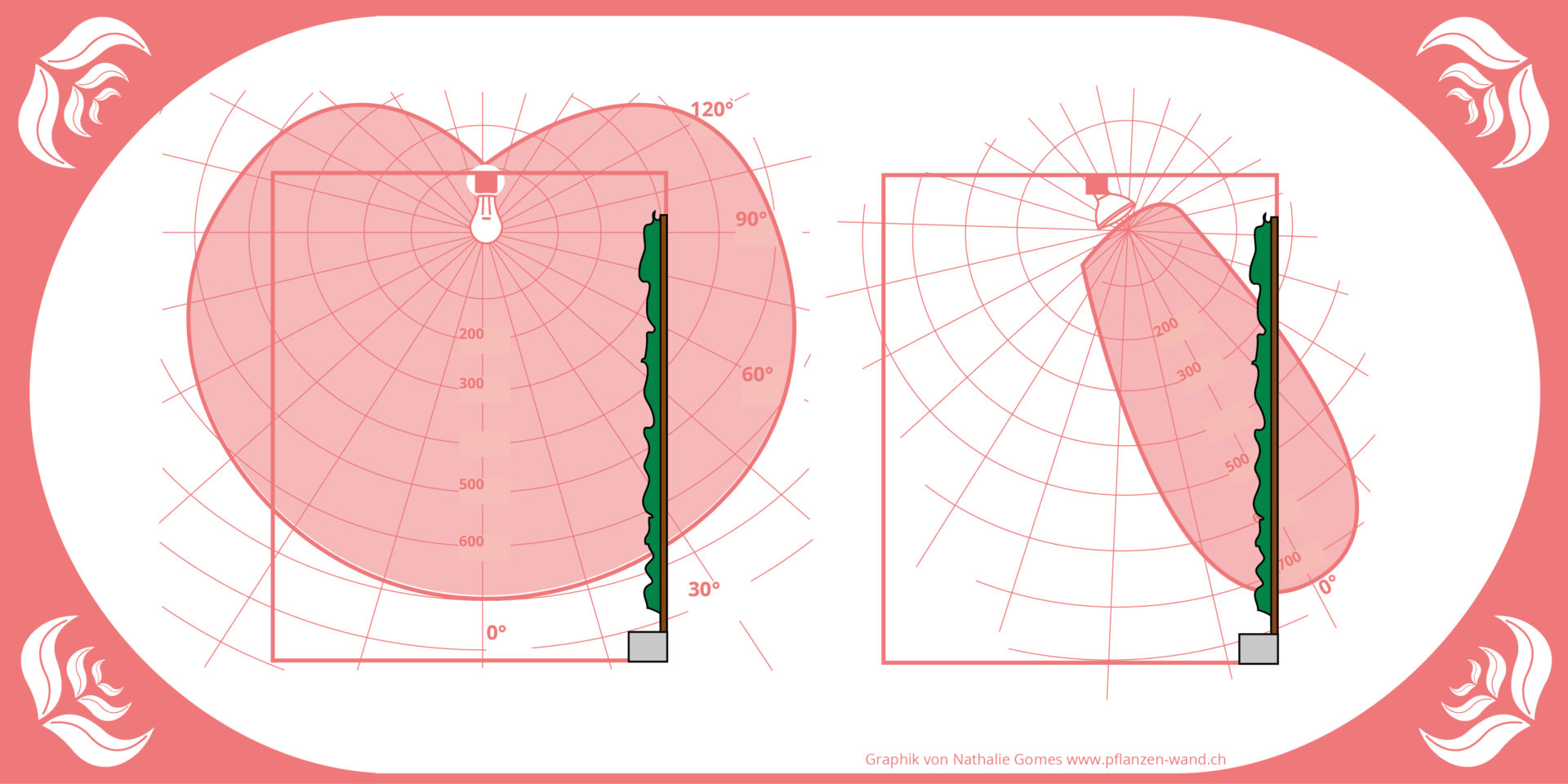
What can be read?
- The one on the left of the light bulb illuminates the whole wall. But all around it, too. This can be a disruptive factor in the apartment and dazzle.
- The light bulb also reflects light from the ceiling. If it is bright.
- With the light bulb in the example, the lowest plants could get a little less light.
- The spot on the right is more efficient and bundles the light into the plant wall. This means that the light output is definitely better.
- Due to the scheme, the angle by attaching the spot should be well appreciated
- At the spot, the upper plants will get a little less light.
My tip
Use light distribution curves to find the right lamp but don’t rely on the specified values as reflections or light-swallowing elimals change the values in the winung.
1 Lux= 1 lumen/m2
Kelvin – Light colour

The colour of the light refers above all to the white light. Because white light is not the same as white light. There are many different light colours that are located between warm and cold light. The color temperature is a measure to determine the color impression of a light source. The light colour respectively Colour temperature is given in Kelvin (K). Der Wert für weißes Licht liegt zwischen 1000 K und 12000K. The higher the Kelvin, the colder the light.
| warm white | below 3300 K | |
| neutral white | 3300–5300 K | |
| Daylight white (also cold white) | over 5300 K |

For plants, the red respectively blue component in the light. Simply put, red light drives plants to grow and blue light keeps plants under control. This is due to the fact that a high proportion of blue in natural light only occurs at midday, when the sun is at its hottest. The plants begin to protect themselves and grow more bushy and stocky. Since stocky and bushy plants are exactly what we want, light from 5300 Kelvin is suitable, but you should also feel comfortable with the lighting mood. Cold white light is therefore not always the right solution. It depends on the sensation of light.
sensation of light
This is the subjective perception of a light. How does the light affect my home and my mood? You can’t judge the feeling of light in front of the store shelf, you should judge it where you need it at the end.
When cold light hits plants, it doesn’t seem so cold anymore because the plants absorb a large part of the blue light.
My tip
I prefer lamps between 4000K and 5000K.
Spectrum (light waves)
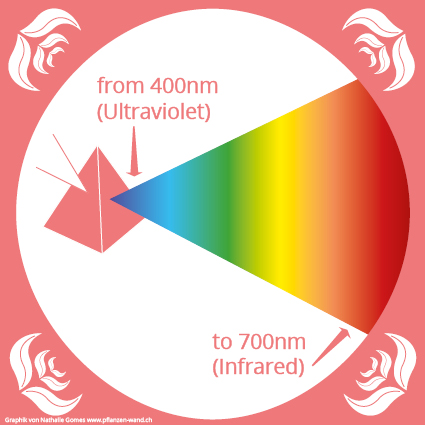
The light spectrum is the sum of all colours that together form a white light. This means that every white light consists of coloured light waves (rays of light). A prism can show the whole rainbow of white light.
When talking about light spectrum, then it means only the ray spectrum that is perceived by our eyes. The radiation spectrum, however, goes much further, such as radar, radio or gamma rays. But in this case we are only interested in visible light, because it’s all about lamps.
The light spectrum ranges from 400 nm (ultraviolet light) to 700 nm (infrared light). A lamp spectrum, i.e. the expression of the different spectra in a light source, provides information on how many parts of the respective colours (waves) are contained. Normally, the light spectrum is represented as a colored curve. These curves can differ enormously, as can be seen in the figure below.

Lamps for plants should have a balanced calm spectrum. Rashes like in the fluorescent tube do not only disturb the plants, but also the people. There should also be a certain amount of blue. The closer a spectrum comes to the daylight spectrum, the better the light is for the plants.
As soon as plants are bred for cultivation, the red and blue areas of the spectrum play an important role. Read more about it: Link Blog Plant Light
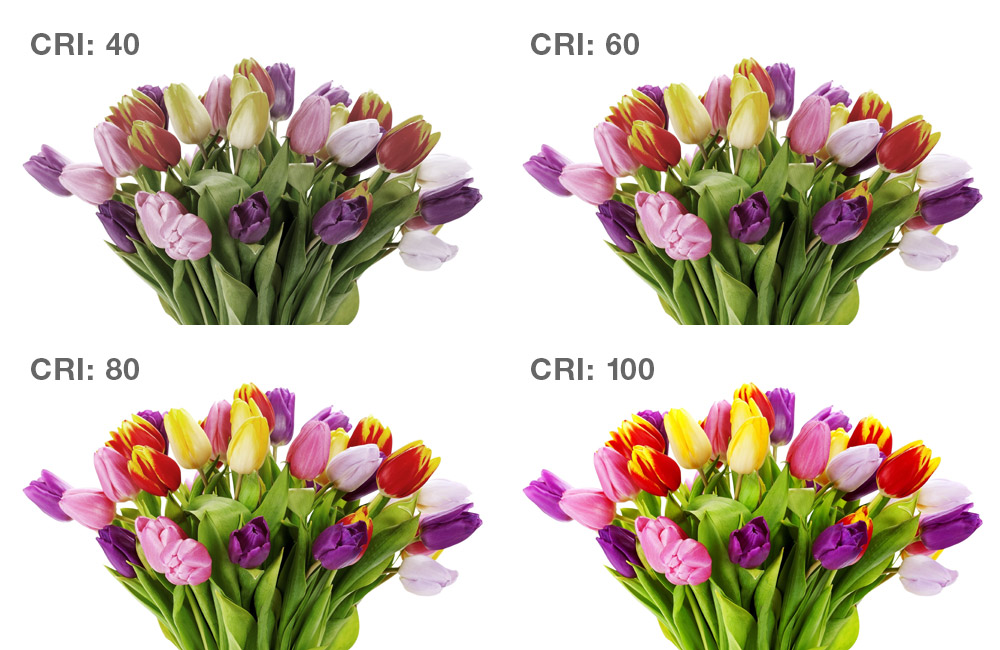
CRI value – colour rendering
CRI(Color Rendering Index) means translated color rendering index and is abbreviated with Ra. The CRI value describes how the color rendering of an artificial light source is compared to sunlight. The maximum value is 100 Ra and does not mean any falsification of the colours by the light.
The CRI value determines how brilliant the colors of the plants are by the light.
In order for the plant wall to be properly effective, the CRI value should in any case be above 90Ra. I prefer lamps with min. 97 Ra.

The sensation
Our perception is very important, because it is a difference how bright, warm or brilliant a light is and how it is perceived individually at the end. This is why we differentiate, for example, between the brightness and the brightness perception of a lamp or the colour rendering index and the colour perception. No matter how great and efficient a lamp is, if you don’t feel comfortable with it, it’s not the right light source. In order to test how you feel in the presence of a light, you should take several lampshome and test them on site. If this is not possible, you can usually also test the lamps in the shop, the ambience is not the same as at home, but it is enough to compare the different lamps with each other. It is best to take a plant with you to see how brilliant the colours of the plantsare and how the colour is reproduced.
In this case you should simply listen to your gut feeling.

My tip
When choosing a lamp, you should ask yourself the following:
- Do I feel comfortable in the light?
- Does the light fit into the ambience (e.g. living room), do I like that?
- Does the color look brilliant and genuine?
- What does a plant look like in the light?
More pages in this post
Creating ambience with light
Creating ambience with light
Click here